The Grasshopper client of Parametric Robot Control was developed exclusively for Rhino 8 on both Windows and macOS. The Rhino 8 .NET Runtime needs to be set to NETCore in the
SetDotNetRuntime command.An early version of a tutorial is available below. The final version will be posted at a later date through the SCALExD project. Refer to the video description to download the used files.
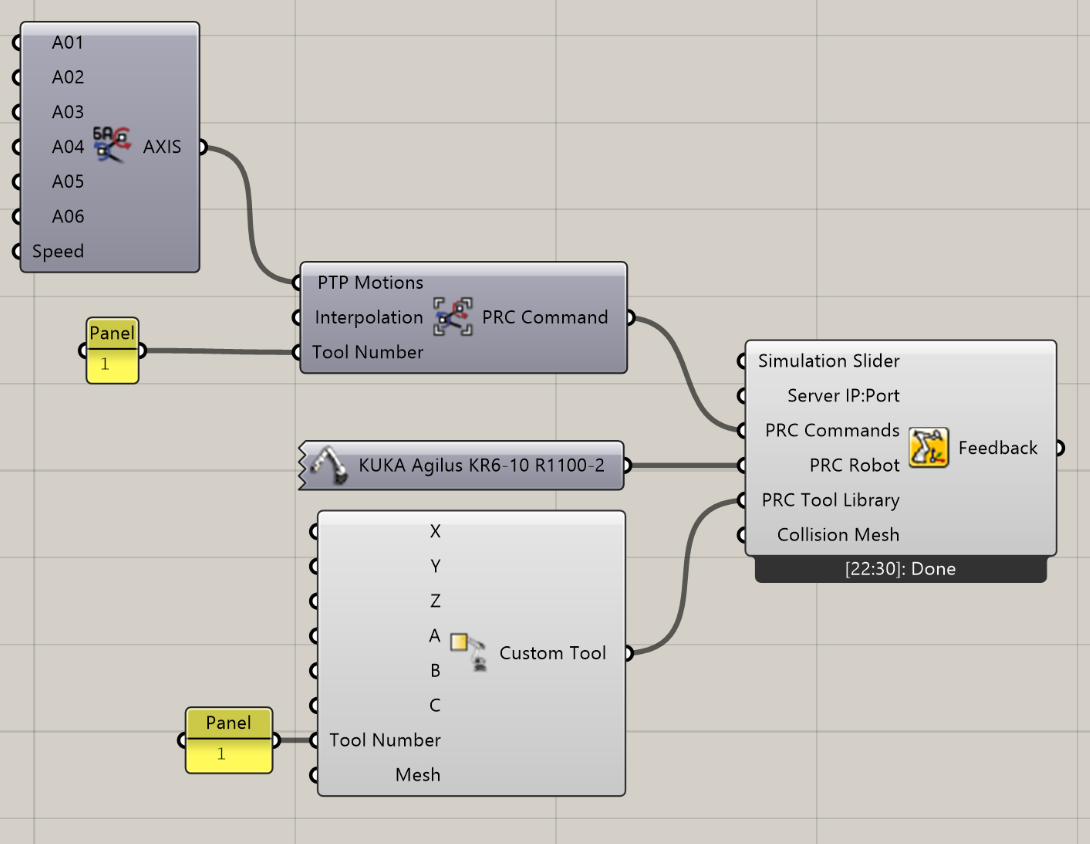
The primary component of PRC in Grasshopper is the Core component, which consumes all the robot process data and formats and forwards it to the server. Then it displays the simulation result.
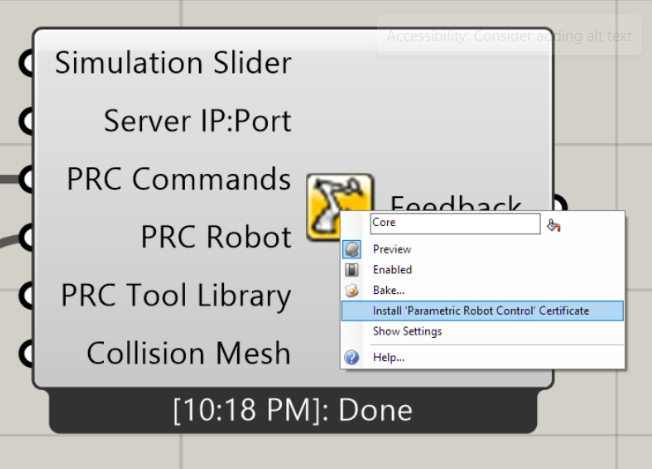
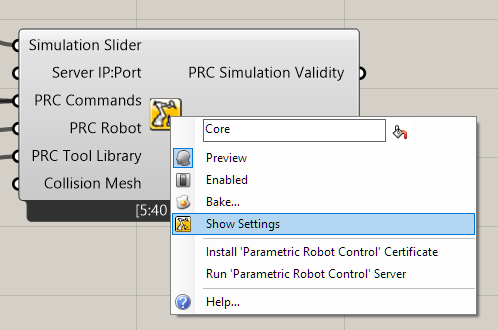
You can right-click the Core component to either install the certificate for encrypted communication, or select "Show Settings" to open a WebView windows in Rhino.
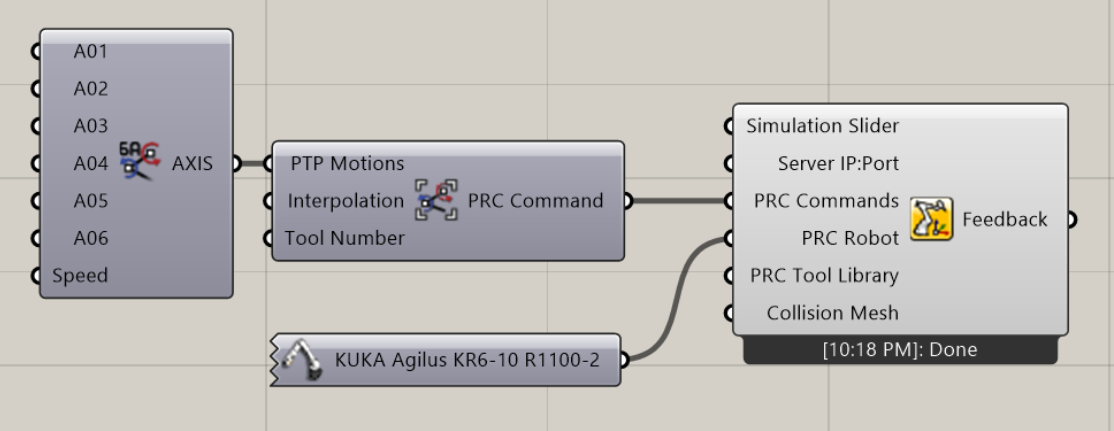
The most simple PRC program consists of a Core component, a robot model, and an Axis motion that is plugged into a PTP Motion Group. Unless otherwise defined, it will use Tool 0 and Base 0, with the default https://localhost:5001 chosen for the server connection.
A more complex program would look as below:
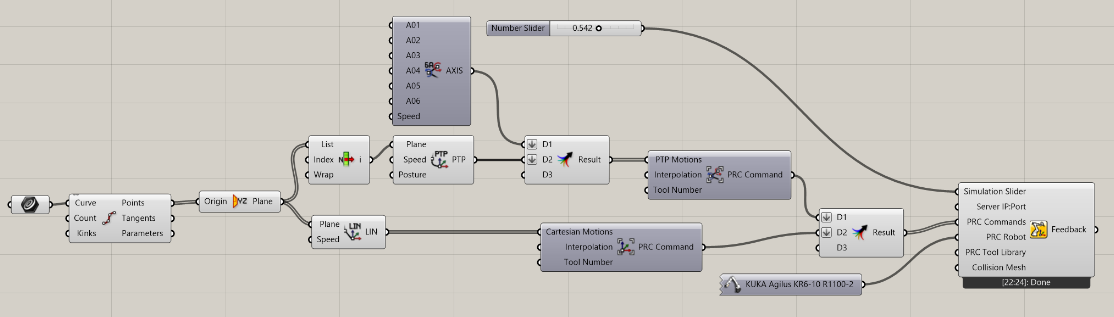
Here, the program starts with an Axis motion. It takes the first position of a toolpath and turns it into a PTP motion with a defined posture. Both are plugged into a PTP Motion Group. The curve itself is followed by a series of LIN motions, plugged into a CP Motion Group.
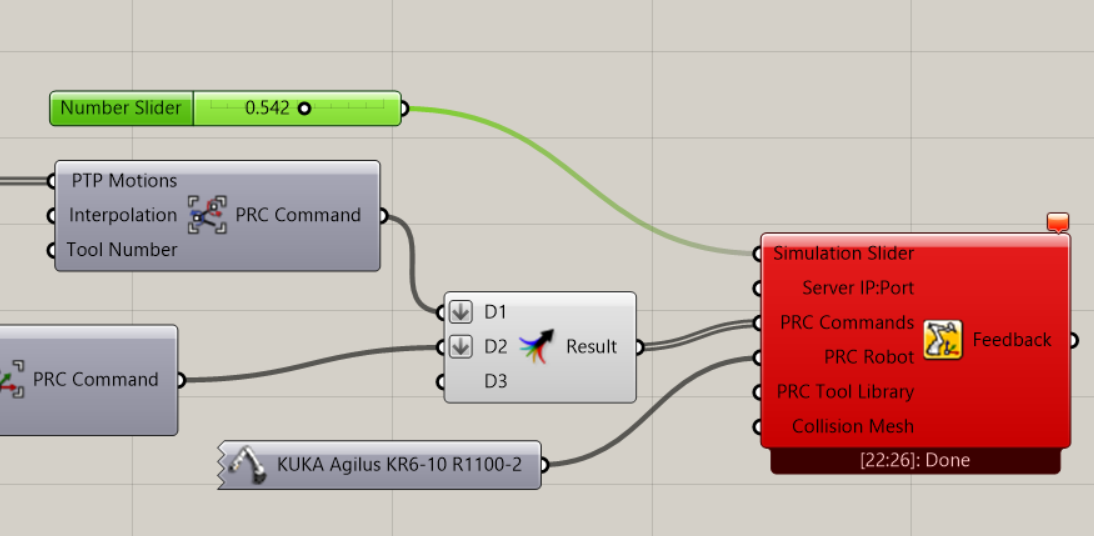
Changing the value of the simulation slider between 0.0-1.0 updates the simulation. If the toolpath contains a non-reachable position, the Core component turns red.
All tools (with the exception of tool 0) have to be plugged into the PRC Tool Library input. The Motion Group then contains only the ID of the tool.
You can access the settings directly through the browser at https://localhost:5001 or alternatively use the embedded browser in Rhino by right-clicking the Core component.
Examples are available in the Sample Projects section.
