The Blender integration is at its core very similar to the  gRPC via Python implementation as it also uses Python as a programming language.
gRPC via Python implementation as it also uses Python as a programming language.
 gRPC via Python implementation as it also uses Python as a programming language.
gRPC via Python implementation as it also uses Python as a programming language.It consists of the following files:
The main code is contained in  gRPC via Python. Similarly, the
gRPC via Python. Similarly, the
init.py while the prc_pb2… files are reused from  gRPC via Python. Similarly, the
gRPC via Python. Similarly, the *.pem files are the encryption certificates for either macOS or other implementations.The
PRC_AgilusTest.blend file contains the robot geometry (without requiring rigging or an armature).Pack the content of the folder into a ZIP file and import it into Blender via Edit > Preferences > Add-ons > Install.
Installing gRPC
You may get an error message that a package is missing
We recommend installing gRPC via https://github.com/luigipacheco/blenderpipinstaller - similar to before, go to Blender Preferences > Add-ons > Install and select the downloaded ZIP file.
Now open a Text edit window and open the sidebar. Select the "Pip Installer" tab. Install the following packages: "grpcio" and "protobuf". Especially protobuf may take a while to install.
Then restart Blender and enable the PRC Add-on again.
It should now be visible in the sidebar.
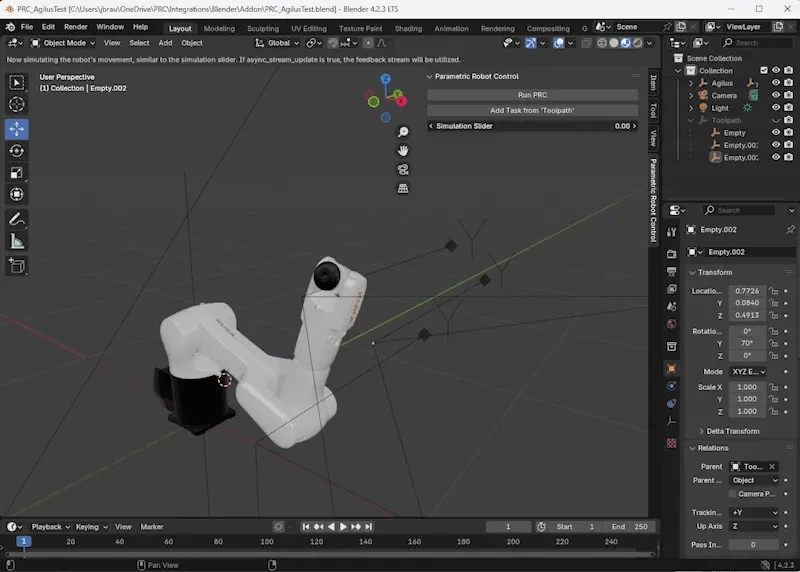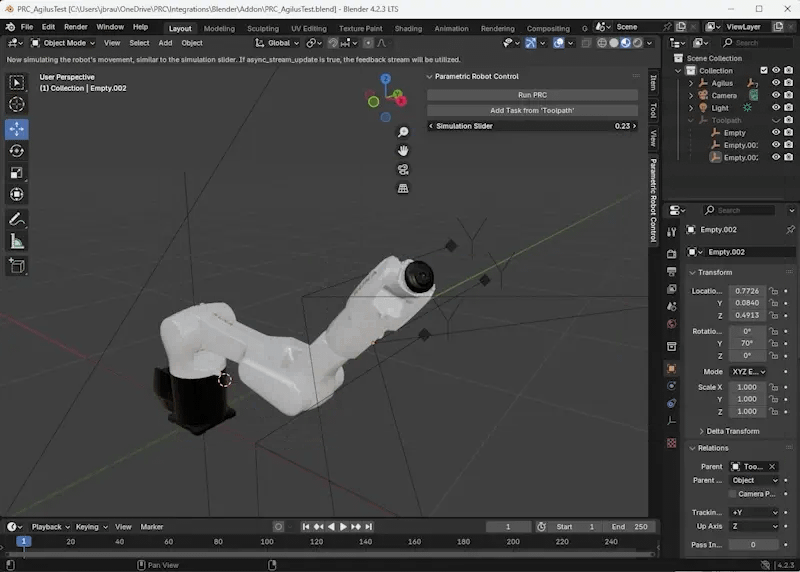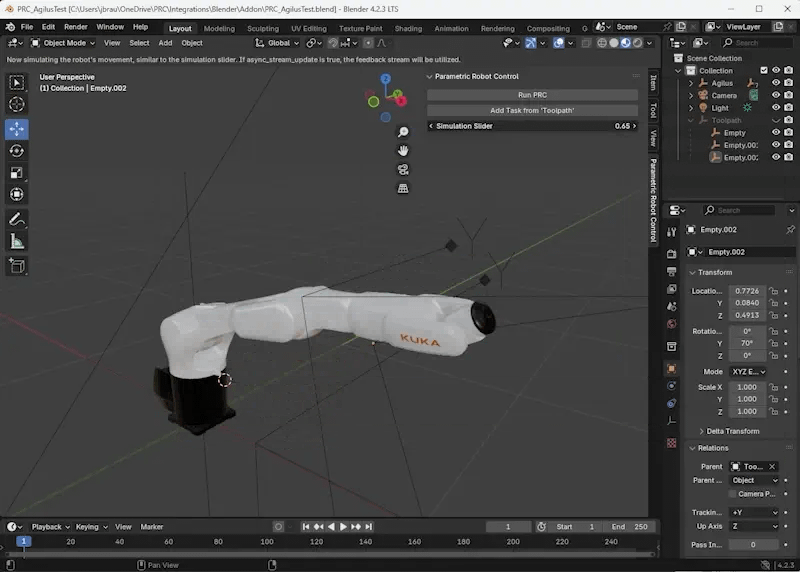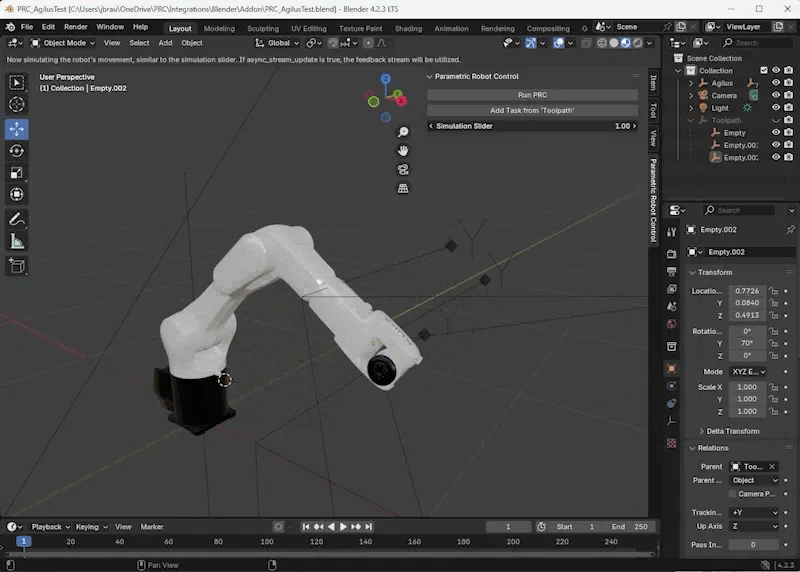
“Run PRC” starts the server, use that one first. It comes with a standard movement that you can then simulate via the “Simulation Slider”.
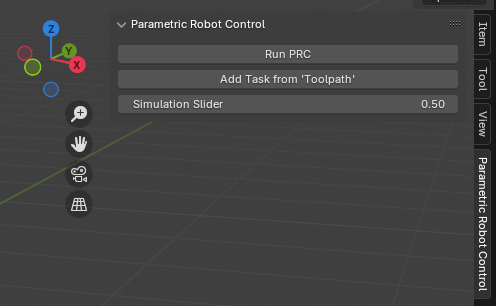
The “Add Task from ‘Toolpath’” button takes the transformations from all objects in the Toolpath group and uses them as Cartesian targets.

Note that the code applies the relevant transformation and also scales everything by a factor 1000 as Blender works better with small units (meters) while the robot expects millimeters.
pythonmotion_list = [] for obj in bpy.data.objects['Toolpath'].children: matrix = obj.matrix_world.copy() matrix.transpose() prc_matrix = prc_pb2.Matrix4x4() prc_matrix.m11 = matrix[0][0] prc_matrix.m12 = matrix[0][1] ... prc_matrix.m41 = matrix[3][0]*1000 prc_matrix.m42 = matrix[3][1]*1000 prc_matrix.m43 = matrix[3][2]*1000 prc_matrix.m44 = matrix[3][3] ptp_motion = prc_pb2.MotionCommand( ptp_motion=prc_pb2.PTPMotion( target=prc_pb2.CartesianTarget( position=prc_pb2.CartesianPosition( matrix=prc_matrix), posture="110", speed=[0.1] ) ) ) motion_list.append(ptp_motion)
The full code is available here:
